Introduction to Uterine Fibroids Treatment
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop within the uterus. While many women with fibroids may not experience any symptoms, others may suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and complications during pregnancy. Understanding the treatment options available is essential for managing these symptoms and improving quality of life. Flowcare offers a range of solutions for women seeking effective uterine fibroids treatment.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
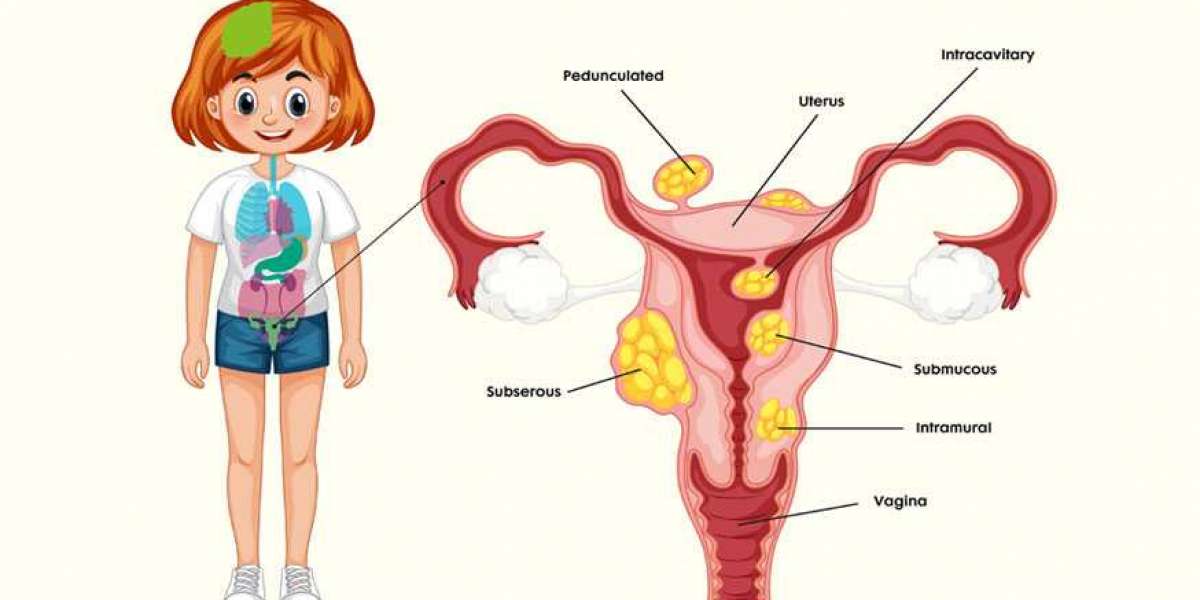
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are benign tumors that originate from the smooth muscle cells of the uterus. They can vary in size from small seedlings to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus. Fibroids are classified based on their location: submucosal (within the uterine cavity), intramural (within the uterine wall), and subserosal (on the outer surface of the uterus).
While the exact cause of fibroids is not well understood, hormonal factors, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a significant role in their growth. Genetics and lifestyle factors, such as obesity and diet, may also influence the development of fibroids.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Not all women with fibroids will experience symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be debilitating and may include heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain, frequent urination, and constipation. In some cases, fibroids can lead to complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage or preterm labor.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids typically involves a pelvic examination and imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI. These tests help determine the size, location, and number of fibroids, which are critical factors in deciding the most appropriate treatment plan.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For women seeking to manage fibroid symptoms without surgery, several non-surgical treatment options are available. These treatments aim to relieve symptoms and reduce the size of fibroids, although they may not eliminate fibroids entirely.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for women with mild to moderate symptoms. Hormonal therapies, such as GnRH agonists, can shrink fibroids by lowering estrogen levels. These medications may be used temporarily to reduce symptoms or as a preoperative measure before surgery.
Other medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs and oral contraceptives, can help manage symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding and pain. However, these treatments do not shrink fibroids and are generally used to control symptoms rather than treat the underlying condition.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure that involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink. During UFE, a radiologist inserts a catheter into the uterine arteries and injects small particles that obstruct blood flow to the fibroids.
UFE is an effective treatment option for women who wish to avoid surgery and preserve their uterus. The procedure is associated with a high success rate and a low risk of complications. Most women experience significant symptom relief after UFE, although it may take several months for the full effects to be realized.
Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS)
Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS) is another non-invasive treatment option for uterine fibroids. This procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue. FUS is performed under MRI guidance, allowing for precise targeting of the fibroids while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
FUS is a safe and effective option for women with symptomatic fibroids who prefer a non-surgical approach. However, it may not be suitable for all types of fibroids, particularly those that are large or located deep within the uterus.
Surgical Treatment Options
When non-surgical treatments are insufficient or when fibroids cause severe symptoms, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery is often recommended for women with large fibroids, those who desire future pregnancies, or those who have not responded to other treatments.
Myomectomy
Myomectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. This procedure is particularly beneficial for women who wish to maintain their fertility. Myomectomy can be performed through various approaches, including hysteroscopic, laparoscopic, or abdominal surgery, depending on the size and location of the fibroids.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy is performed through the vagina and cervix and is suitable for removing submucosal fibroids. Laparoscopic myomectomy involves small incisions in the abdomen and is ideal for removing intramural and subserosal fibroids. Abdominal myomectomy, also known as an open myomectomy, is used for large or multiple fibroids that cannot be removed through minimally invasive techniques.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, is the most definitive treatment for uterine fibroids. This procedure is usually considered when other treatments have failed, when fibroids are extremely large, or when the woman has completed childbearing.
There are several types of hysterectomy, including total hysterectomy (removal of the entire uterus), subtotal hysterectomy (removal of the upper part of the uterus, leaving the cervix in place), and radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus, cervix, and surrounding tissues). The choice of procedure depends on the severity of the symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the patient's preference.
While hysterectomy effectively eliminates fibroids and their associated symptoms, it is a major surgery with potential risks and complications. Women considering this option should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
In addition to conventional medical treatments, some women explore alternative and complementary therapies to manage fibroid symptoms. These treatments include dietary changes, herbal supplements, acupuncture, and stress management techniques.
While there is limited scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of these therapies, some women report symptom relief and improved well-being. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatments, as they may interact with other medications or have unintended side effects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Uterine Fibroids Treatment
Choosing the right uterine fibroids treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the woman's reproductive goals. At Flowcare, we are committed to providing personalized care and helping women navigate their treatment options.
Whether you prefer a non-surgical approach or require surgical intervention, Flowcare offers a range of effective solutions to manage uterine fibroids and improve your quality of life. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can find the best treatment plan to address your specific needs and achieve optimal uterine health.