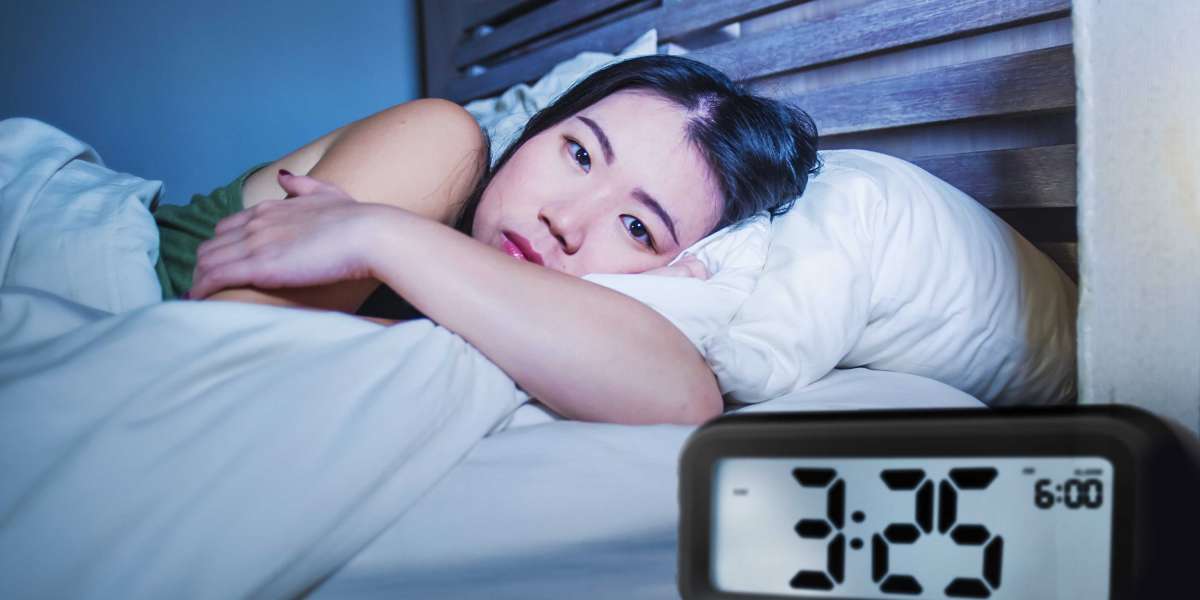
Insomnia, a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early, affects many young adults and teens. With a myriad of changes happening during adolescence—physically, emotionally, and socially—sleep disturbances can often become a significant challenge. Understanding the factors contributing to insomnia in this age group and exploring effective solutions is crucial for improving their overall well-being.
The Importance of Sleep for Teens
Sleep is vital for everyone, but it is especially critical for teenagers. Adolescence is a developmental phase marked by rapid growth and changes. During this time, adequate sleep supports cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and physical health. Studies suggest that teens require about 8 to 10 hours of sleep per night to function optimally. Sleep deprivation can lead to various issues, including academic struggles, mood disorders, and increased risk of physical health problems.
Factors Contributing to Insomnia in Teens
1. Biological Changes
As teens grow, their circadian rhythms—the internal biological clock that regulates sleep-wake cycles—shift. This shift often causes them to feel more alert in the evening and sleepy later at night. Unfortunately, early school start times can clash with their natural sleep patterns, making it difficult for them to get the required amount of sleep.
2. Academic Pressure
The pressure to perform well academically can lead to increased stress and anxiety among teens. Homework, exams, and extracurricular activities can consume valuable time that should be dedicated to sleep. Many teens sacrifice sleep in favor of studying or completing assignments, which can lead to a cycle of insomnia and fatigue.
3. Mental Health Issues
Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, are prevalent among adolescents and can significantly impact sleep. Teens experiencing high levels of stress, worry, or sadness may find it challenging to relax at bedtime, leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night.
4. Technology and Screen Time
In today’s digital age, screen time has increased significantly among teens. The blue light emitted by smartphones, tablets, and computers can interfere with the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. Many teens engage in late-night screen time, making it harder for them to unwind and fall asleep.
5. Lifestyle Choices
Dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and irregular sleep schedules also contribute to insomnia symptoms in teens. Consuming caffeine or sugary snacks, particularly in the hours leading up to bedtime, can disrupt sleep patterns. Furthermore, a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate feelings of restlessness and anxiety.
Signs of Insomnia in Teens
Recognizing the signs of insomnia is crucial for timely intervention. Common indicators include:
Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
Waking up frequently during the night
Excessive daytime sleepiness
Irritability or mood swings
Difficulty concentrating or focusing in school
A reliance on caffeine or stimulants to stay awake
How to Help Teens Combat Insomnia
1. Encourage Healthy Sleep Hygiene
Promoting good sleep hygiene can significantly improve a teen’s sleep quality. This includes:
Encourage teens to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate their internal clock.
Activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques can help signal to the body that it’s time to wind down.
Encourage teens to turn off electronic devices at least an hour before bedtime to reduce blue light exposure.
2. Address Academic Stress
Helping teens manage academic pressure is essential for promoting better sleep. Strategies include:
Teach teens to prioritize tasks and break assignments into manageable chunks, allowing them to balance academics and sleep more effectively.
Foster an environment where teens feel comfortable discussing their academic pressures and stressors. This support can alleviate feelings of anxiety.
3. Promote Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can enhance sleep quality. Encourage teens to engage in at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week. Activities can include sports, dancing, or even walking. However, it's important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may have a stimulating effect.
4. Monitor Caffeine and Sugar Intake
Help teens become aware of their dietary choices, particularly in relation to caffeine and sugar consumption. Encourage them to limit these substances, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Instead, promote healthier snack options, such as fruits or nuts, for late-night cravings.
5. Seek Professional Help if Necessary
If insomnia persists despite implementing these strategies, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can assess the situation and recommend therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or medication if appropriate.
In summary
Insomnia is a significant issue among teens, often stemming from a combination of biological, psychological, and lifestyle factors. By understanding the causes and implementing effective strategies, parents, educators, and healthcare providers can help young adults overcome sleep difficulties. Promoting healthy sleep habits not only enhances academic performance but also fosters emotional well-being, ultimately leading to a healthier and happier adolescence.