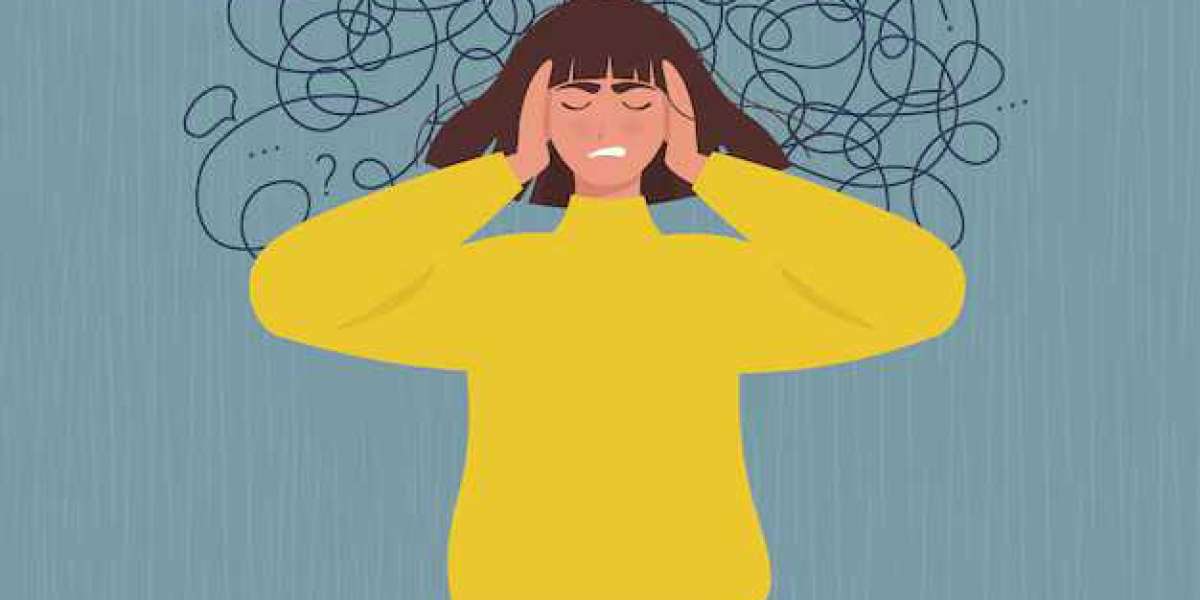
Self-image anxiety, also known as appearance anxiety, is a constant worry about how you look and the fear of being judged negatively for it. It's more than just occasional insecurity. People with self-image anxiety are preoccupied with perceived flaws, both real and imagined. This fixation can lead to intense anxiety in social situations, making it difficult to go out in public or even leave the house. Daily activities like getting dressed can become stressful because of the fear of being scrutinized. This anxiety can significantly impact a person's self-esteem, social life, and overall well-being.
What mental disorders affect self-image anxiety
Many mental health conditions can warp how you see yourself and trigger self-image anxiety about your self-image. Others, like Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), cause your self-image to be unstable, shifting rapidly and fueling anxiety. Even social anxieties, where you fear judgment in social situations, can distort your self-image and make you feel constantly scrutinized.
The Impact of Self-Image Anxiety on Mental Health?
If you're experiencing fear related to self-image anxiety and its impact on mental health, seeking help and guidance from the “Best psychologist near me” can support your recovery and well-being.
- Low Self-Esteem: Body dissatisfaction can contribute to low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy.
- Depression: Persistent self-image anxiety may lead to depressive symptoms, such as sadness and hopelessness.
- Social Anxiety: Fear of negative evaluation based on appearance can result in social anxiety and avoidance of social interactions.
- Body Dysmorphic Thoughts: Self-doubt may manifest as body dysmorphic thoughts, causing obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws.
- Avoidance Behaviors: Individuals may engage in avoidance behaviors to conceal perceived flaws, impacting social and occupational functioning.
- Negative Body Image: Poor self-esteem is often associated with a negative body image, leading to dissatisfaction with one's physical appearance.
- Impaired Relationships: Social insecurity can strain relationships due to heightened self-consciousness and insecurity.
- Perfectionism: Striving for unrealistic beauty standards can contribute to perfectionistic tendencies and dissatisfaction with oneself.
- Problems with Eating:-Anorexia nervosa and bulimia are two eating disorders that may develop as a result of severe social fear.
- Compulsive Behaviors: Some individuals with self-image anxiety may engage in compulsive behaviors like excessive grooming or mirror-checking.
- Sleep Disturbances: Heightened anxiety about self-image can lead to sleep disturbances and insomnia.
- Impact on Academic or Work Performance: Self-consciousness can distract from academic or work tasks, affecting productivity and performance.
- Co-occurring Mental Health Conditions: Low self-worth often coexists with other mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders or body dysmorphic disorder (BDD).
- Reduced Self-Confidence: Overall, Shyness can undermine self-confidence and hinder personal growth and fulfillment.
- Negative Coping Strategies: Some individuals may resort to unhealthy coping strategies such as substance abuse to manage self-image anxiety.
- Isolation: Severe self-image anxiety may lead to social withdrawal and isolation, impacting social support networks and mental well-being.
It's important to address self-image anxiety and seek support from mental health professionals "Online counselor" to develop healthier coping strategies and improve overall well-being.
How to Recognize and Manage Self-Image Anxiety?
Recognizing and managing self-image anxiety involves several key strategies. Here are to help identify and cope with Low self-worth:
- Awareness of Negative Thoughts: Recognize and challenge negative thoughts about your appearance.
- Identify Triggers: Identify situations or triggers that intensify feelings of self-image anxiety.
- Monitor Body Checking Behaviors: Be mindful of compulsive behaviors like excessive mirror-checking or body scrutiny.
- Seek Feedback from Trusted Individuals: Ask for feedback from supportive and trusted individuals to gain perspective.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Treat yourself with kindness and understanding, focusing on your strengths.
- Limit Exposure to Media: Reduce exposure to media that promotes unrealistic beauty standards.
- Develop Healthy Coping Skills: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as meditation or exercise.
- Challenge Perfectionism: Set realistic expectations and accept imperfections as part of being human.
- Focus on Health: Shift focus from appearance to overall health and well-being through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
- Set Boundaries: Establish boundaries with others to prevent negative comments or behaviors that trigger self-image anxiety.
- Practice Mindfulness: Stay present in the moment and observe thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Engage in Positive Affirmations: Repeat affirmations that promote self-acceptance and self-esteem.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult a psychologist or therapist specializing in body image issues for guidance and support.
- Challenge Avoidance Behaviors: Gradually confront situations that trigger anxiety rather than avoiding them.
- Develop a Support System: Surround yourself with supportive friends and family who uplift and encourage you.
- Focus on Personal Growth: Set goals and pursue activities that promote personal growth and fulfillment beyond appearance.
conclusion
Self-image anxiety is a complex issue that can have profound effects on mental well-being and daily life.