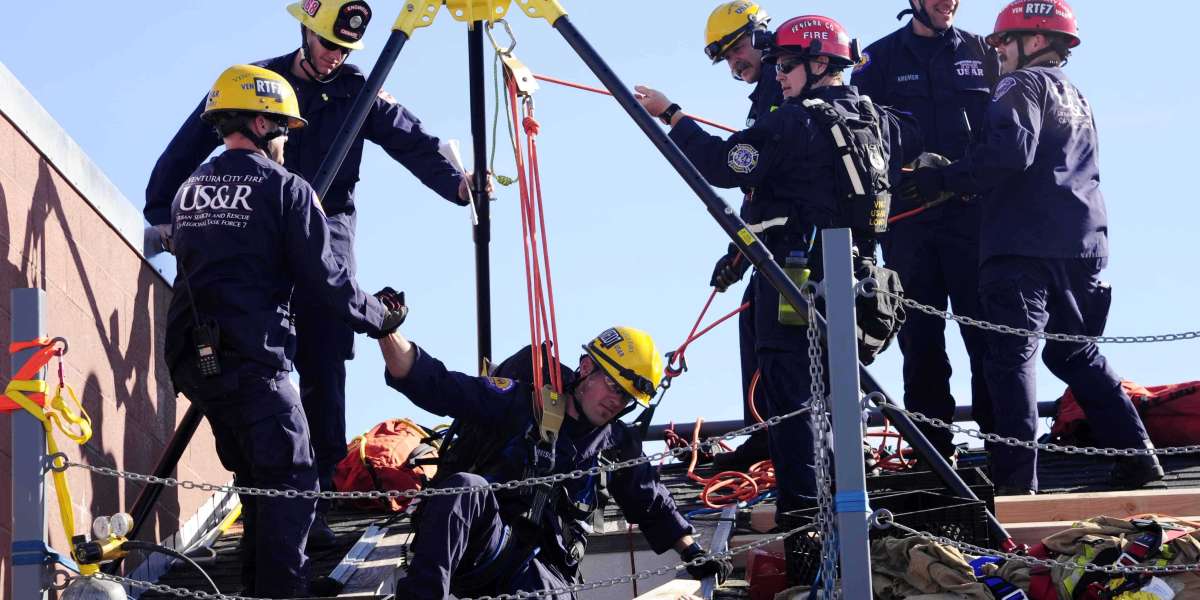
Ensuring safety in confined spaces is a critical concern for industries such as construction, manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Confined spaces pose unique risks, including hazardous atmospheres, limited entry and exit points, and restricted movement, making them potentially deadly if not managed correctly. Advanced monitoring systems have become indispensable tools for mitigating these risks and safeguarding the lives of workers. This article explores the importance of safety in confined spaces and the role of advanced monitoring systems, with a focus on the comprehensive training provided by an IOSH Course. Additionally, we will touch upon IOSH Course fees in Pakistan to offer a detailed perspective on the cost of acquiring such crucial safety skills.
Understanding Confined Spaces
1. What Are Confined Spaces?
Confined spaces are areas that are not designed for continuous occupancy. They have limited means of entry and exit and may contain hazardous conditions. Examples include tanks, silos, manholes, and pipelines. These environments can present significant risks such as oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, explosive atmospheres, and physical hazards.
2. Hazards Associated with Confined Spaces
Confined spaces can be hazardous due to:
- Atmospheric hazards: Toxic gases, vapors, or oxygen-deficient atmospheres.
- Physical hazards: Limited entry and exit points, poor lighting, and structural instability.
- Engulfment hazards: The risk of being engulfed by materials like grain, sand, or liquids.
- Temperature extremes: High or low temperatures that can affect workers' health and performance.
Understanding these hazards is the first step towards mitigating risks and ensuring safety.
The Role of Advanced Monitoring Systems in Ensuring Safety
1. What Are Advanced Monitoring Systems?
Advanced monitoring systems use modern technology to detect and manage hazards in confined spaces. These systems include gas detectors, environmental sensors, real-time monitoring software, and communication tools. By providing continuous data on the conditions inside confined spaces, these systems help ensure the safety of workers by alerting them to potential dangers.
2. Types of Monitoring Systems
- Gas Detection Systems: These systems detect harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and methane. They provide real-time data on gas levels, enabling prompt action to avoid exposure.
- Environmental Monitoring Systems: These systems monitor temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions to ensure they remain within safe limits.
- Remote Monitoring Systems: These systems allow off-site monitoring of confined spaces, providing real-time data to supervisors and safety personnel. This feature is crucial for quick decision-making in emergencies.
- Communication Systems: Reliable communication is vital in confined spaces. Advanced systems ensure constant contact between workers inside the confined space and the safety team outside.
Benefits of Advanced Monitoring Systems
- Real-time Data: Continuous monitoring provides up-to-the-minute information on the conditions inside confined spaces, allowing for immediate action if hazards are detected.
- Improved Safety: By detecting hazards early, these systems help prevent accidents and protect workers' lives.
- Compliance: Advanced monitoring systems help companies comply with safety regulations and standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties.
- Efficiency: Automated systems reduce the need for manual checks, saving time and resources.
Implementing Advanced Monitoring Systems: Best Practices
1. Conducting a Thorough Risk Assessment
Before implementing any monitoring system, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment. This involves identifying potential hazards, evaluating the risks, and determining the appropriate monitoring solutions.
2. Selecting the Right Equipment
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for effective monitoring. Factors to consider include:
- Type of Confined Space: Different spaces require different types of monitoring systems.
- Hazards Present: The equipment must be capable of detecting specific hazards associated with the confined space.
- Durability and Reliability: The equipment should be robust and reliable, capable of operating in harsh conditions.
3. Training and Competence
Ensuring that workers are properly trained to use monitoring equipment is vital. This includes:
- Proper Use: Understanding how to operate the equipment correctly.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and calibration to ensure accuracy.
- Emergency Response: Knowing how to respond to alarms and emergencies effectively.
4. Continuous Improvement
Safety in confined spaces requires continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments, monitoring systems, and safety procedures. Feedback from workers and incident reports can provide valuable insights for improving safety measures.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Advanced Monitoring Systems
Case Study 1: Oil and Gas Industry
An oil and gas company implemented advanced gas detection systems in their storage tanks. The system provided real-time data on gas levels and alerted workers to potential hazards. As a result, the company saw a significant reduction in incidents and improved compliance with safety regulations.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Sector
A manufacturing plant introduced remote monitoring systems for their confined spaces. This allowed supervisors to monitor conditions from a central control room, enhancing their ability to respond quickly to emergencies. The system also helped in identifying areas for improvement in their safety protocols.
Case Study 3: Utility Services
A utility service provider installed environmental monitoring systems in their underground utilities. The system continuously monitored temperature and humidity levels, ensuring they remained within safe limits. This proactive approach prevented heat stress and other environmental hazards, ensuring worker safety.
Future Trends in Confined Space Safety
1. Integration with IoT and AI
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing confined space safety. IoT devices can provide real-time data on various environmental parameters, while AI can analyze this data to predict potential hazards and recommend preventive measures.
2. Enhanced Communication Technologies
Advancements in communication technologies are improving connectivity in confined spaces. Enhanced communication systems ensure constant contact between workers and safety personnel, facilitating quick and efficient responses to emergencies.
3. Wearable Technology
Wearable technology, such as smart helmets and sensors, is gaining popularity in confined space safety. These devices can monitor vital signs, environmental conditions, and worker location, providing an additional layer of safety.
4. Regulatory Changes
Regulations and standards for confined space safety are continually evolving. Staying updated with these changes is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring worker safety. Organizations must adapt to new regulations by updating their safety protocols and investing in the latest monitoring technologies.
Importance of Training in Confined Space Safety
1. The IOSH Course: A Comprehensive Training Solution
The Institution of Occupational Safety and Health (IOSH) offers courses designed to equip workers with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage safety in confined spaces. An IOSH Course covers various aspects of health and safety, providing a thorough understanding of risk assessment, hazard management, and emergency procedures.
2. Key Components of an IOSH Course
- Risk Assessment: Training on identifying potential hazards and assessing the risks associated with confined spaces.
- Emergency Procedures: Developing and practicing emergency response plans to ensure quick and effective action in case of an incident.
- Use of Monitoring Equipment: Hands-on training in using advanced monitoring systems to detect and manage hazards.
- Legal Compliance: Understanding regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
3. IOSH Course Fees in Pakistan
The IOSH Course fees in Pakistan can vary depending on the provider and the level of training offered. On average, the fees range from PKR 20,000 to PKR 50,000. Investing in this training is crucial for ensuring the safety of workers and maintaining a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Ensuring safety in confined spaces is a complex and challenging task that requires a comprehensive approach. Advanced monitoring systems play a crucial role in detecting hazards and protecting workers' lives. By investing in these technologies and providing thorough training through an IOSH Course, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with confined spaces. The cost of such training, including IOSH Course fees in Pakistan, is a small price to pay for the invaluable benefit of saving lives and ensuring a safe working environment. Continuous improvement and adaptation to new technologies and regulations are essential for maintaining high safety standards in confined spaces.