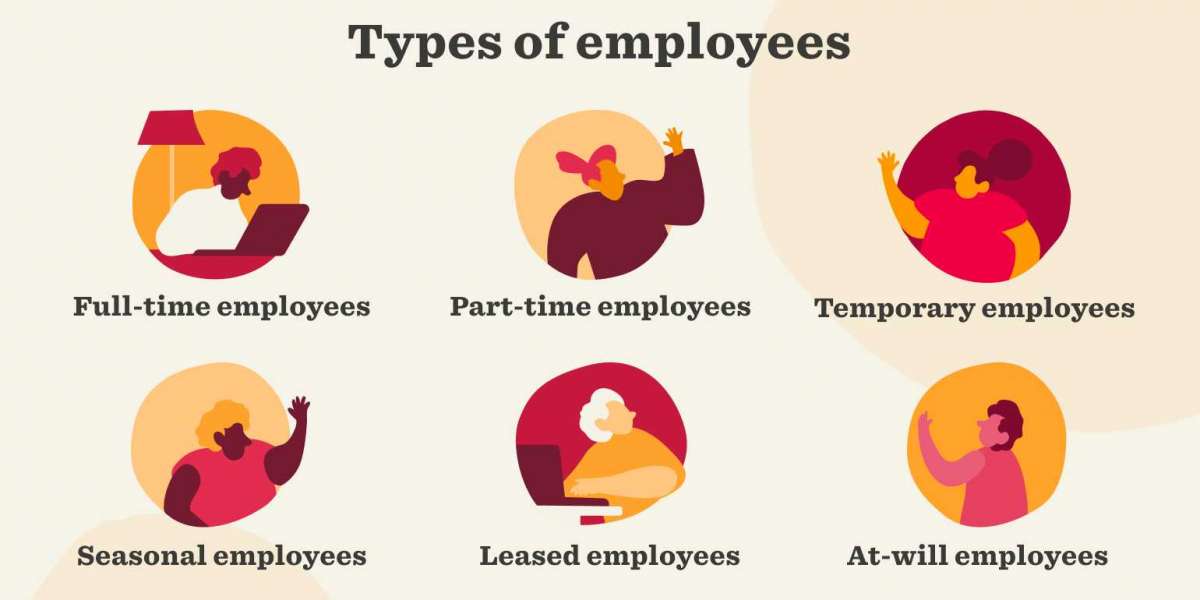
The employment landscape has evolved significantly, offering a variety of work arrangements to meet the diverse needs of both employers and employees. Understanding the different types of employment is crucial for making informed career decisions and optimizing workforce management. This blog explores the various types of employment, highlighting their unique features, benefits, and challenges.
1. Full-Time Employment
Full-time employment typically involves working a standard 40-hour week, though this can vary by industry and company. Full-time employees often receive a range of benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and job security.
Benefits
- Stability: Full-time positions offer consistent work schedules and income.
- Benefits: Access to comprehensive benefits packages.
- Career Growth: Opportunities for advancement within the company.
Challenges
- Work-Life Balance: May require long hours, impacting personal time.
- Less Flexibility: Fixed schedules may limit personal and professional flexibility.
2. Part-Time Employment
Part-time employees work fewer hours than full-time employees, often less than 30 hours per week. This type of employment is ideal for individuals seeking flexibility or supplementary income.
Benefits
- Flexibility: More control over work hours, allowing for better work-life balance.
- Supplementary Income: Ideal for students, retirees, or those with other commitments.
- Experience: Opportunity to gain experience in a particular field.
Challenges
- Fewer Benefits: Part-time positions often offer limited or no benefits.
- Less Stability: Inconsistent hours and income.
3. Temporary Employment
Temporary employment involves working for a limited period, often through a staffing agency. Temporary workers fill short-term needs, such as seasonal peaks, special projects, or employee absences.
Benefits
- Short-Term Commitment: Ideal for those seeking temporary work or testing different career paths.
- Skill Development: Opportunity to gain experience in various industries.
- Networking: Build professional connections in different workplaces.
Challenges
- Lack of Job Security: Employment ends when the contract expires.
- Limited Benefits: Often no access to company benefits.
- Inconsistency: Work availability can be unpredictable.
4. Contract Employment
Contract employees are hired for specific projects or periods, often possessing specialized skills. They work under a contract that outlines the terms and duration of their employment.
Benefits
- Specialization: Focus on projects that match your skills and interests.
- Higher Pay: Often higher hourly rates due to specialized skills.
- Independence: Greater control over work assignments and schedules.
Challenges
- No Job Security: Employment is project-based and temporary.
- Self-Employment Taxes: Responsible for your own taxes and benefits.
- Inconsistent Work: Potential gaps between contracts.
5. Freelance Employment
Freelancers are self-employed individuals who offer services to multiple clients. They have the flexibility to choose projects, set their rates, and manage their schedules.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Control over work hours and projects.
- Diverse Opportunities: Work with various clients across different industries.
- Independence: Be your own boss and set your rates.
Challenges
- Inconsistent Income: Variable workload can lead to irregular earnings.
- No Benefits: Responsible for securing personal health insurance and retirement plans.
- Self-Discipline: Requires strong time management and self-motivation skills.
6. Internship
Internships are short-term work experiences offered to students or recent graduates. Interns gain practical experience in their field of study, often receiving academic credit or a stipend.
Benefits
- Experience: Gain hands-on experience in a specific industry.
- Networking: Build connections with professionals and potential employers.
- Skill Development: Develop practical skills relevant to your career.
Challenges
- Limited Pay: Internships may offer low pay or be unpaid.
- Temporary: Usually lasts only a few months.
- Entry-Level Tasks: May involve less challenging or routine tasks.
7. Seasonal Employment
Seasonal employment involves working during specific times of the year, such as holidays or peak business periods. Common in industries like retail, tourism, and agriculture.
Benefits
- Short-Term Commitment: Perfect for those looking for temporary work.
- Extra Income: Opportunity to earn additional income during busy seasons.
- Experience: Gain experience in different industries.
Challenges
- Temporary Nature: Employment ends when the season concludes.
- Limited Benefits: Often no access to benefits.
- Intense Work Periods: Can be demanding during peak times.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of employment can help you make informed career choices and manage your workforce effectively. Each employment type offers unique benefits and challenges, catering to different needs and preferences. Whether you seek stability, flexibility, or specialized opportunities, there is an employment type suited to your goals and lifestyle.